Adoption Lifecycle
The ESG adoption lifecycle is a framework that helps organizations understand the process of integrating ESG considerations into their business strategies and operations. It involves five stages:
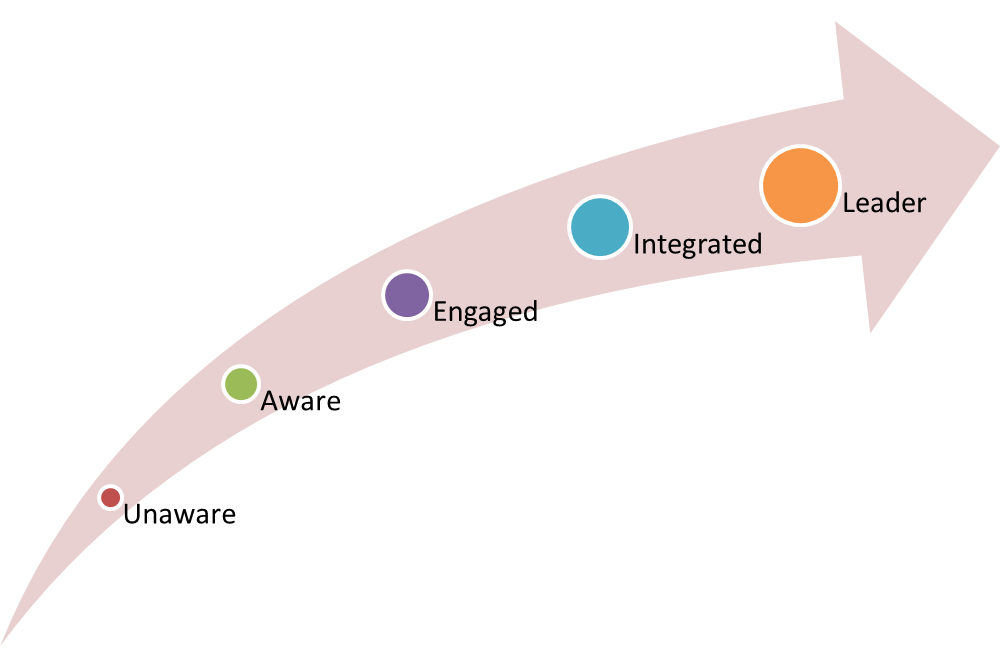
- Unaware: Organizations are not familiar with ESG concepts or their potential impact on their business.
- Aware: Organizations become aware of ESG and start to gather information about its relevance to their industry and stakeholders.
- Engaged: Organizations begin to assess their current ESG performance and identify areas for improvement.
- Integrated: ESG considerations are embedded into the organization’s core business strategy, decision-making processes, and operations.
- Leadership: Organizations become leaders in ESG practices, setting benchmarks and influencing others in their industry.
Organizations can move through the ESG adoption lifecycle at different speeds, depending on their internal factors (such as leadership commitment, resources, and culture) and external factors (such as industry trends, regulatory requirements, and stakeholder expectations).
Here’s a more detailed description of each stage:
Stage 1: Unaware
Organizations at this stage are not aware of ESG concepts or their potential impact on their business. They may not see ESG as a relevant topic for their industry or believe that it is only for large corporations.
Stage 2: Aware
Organizations at this stage become aware of ESG and start to gather information about its relevance to their industry and stakeholders. They may attend ESG conferences or webinars, read ESG reports, or hire consultants to help them understand ESG issues.
Stage 3: Engaged
Organizations at this stage begin to assess their current ESG performance and identify areas for improvement. They may conduct an ESG risk assessment, develop an ESG policy, or set ESG goals.
Stage 4: Integrated
ESG considerations are embedded into the organization’s core business strategy, decision-making processes, and operations. This means that ESG is not just an afterthought, but is considered at every stage of the business, from product development to supply chain management to marketing and communications.
Stage 5: Leadership
Organizations at this stage become leaders in ESG practices, setting benchmarks and influencing others in their industry. They may share their ESG best practices with others, collaborate on industry-wide ESG initiatives, or advocate for ESG policies at the government level.
It is important to note that the ESG adoption lifecycle is not linear. Organizations may move back and forth between stages as they learn more about ESG and as their priorities change. Additionally, organizations may not progress through all stages of the lifecycle. For example, a small, family-owned business may never become a leader in ESG practices, but it can still make significant progress by integrating ESG considerations into its operations.